What insulation is better to use for a mansard roof? Attic insulation: inside, outside, materials
Today we will get acquainted with the most common thermal insulation materials at the moment that can be used for thermal insulation of the attic. This will help you make right choice considering their pros and cons.
Insulation of the attic will allow you to turn the space into a full-fledged living space.
Types of heaters
Currently, the following types of heat are most popular insulating materials:
Option 1: Styrofoam
Expanded polystyrene or simply polystyrene belongs to the category of polymer insulation. Today it is one of the most common heaters, which is used for both indoor and outdoor work.
Advantages:
- low thermal conductivity- coefficient is 0.036-0.050 W/(m°C). Let me remind you that the lower the thermal conductivity, the better;
- light weight- material density is within 15-25kg/m3;
- low cost- Styrofoam is one of the most inexpensive heaters suitable for attic insulation.
Cons of this heater for mansard roof also has quite a few.
Flaws:
- Flammability. Despite the assurances of manufacturers who claim that the foam only melts under the influence of high temperature, in fact, most often it burns. Moreover, it ignites easily and is difficult to extinguish, which I have personally seen more than once.
In the process of burning, it releases toxins into the environment that can lead to serious poisoning; - Zero vapor permeability. After warming attic space, the walls stop "breathing". This leads to an increase in indoor humidity, the formation of condensation on surfaces and, as a result, the appearance of mold. To prevent this from happening, after insulating the attic, it is necessary to ensure high-quality ventilation of the attic;
- Low strength. The insulation is easy to break during transportation or installation.
Contrary to popular belief, foam absorbs moisture, although to a lesser extent than mineral heaters. Water absorption averages 2% of the volume in 24 hours.
Therefore, it makes sense to insulate the mansard roof with foam plastic only if you want to save money or are going to insulate housing for temporary residence, for example, country house. For thermal insulation of the attic of the house in which you will live permanently, I would recommend paying attention to other thermal insulation materials.
Price. Depends on the brand of insulation:
It is better to use the lowest grade foam for the attic - PSB S-15, since it will not be loaded. The advantage of this brand is not only low cost, but also low thermal conductivity.
Option 2: Extruded Styrofoam
Extruded polystyrene foam or simply penoplex, like ordinary polystyrene foam, is a polymer insulation. Its differences lie in a special manufacturing technology, due to which the material has higher characteristics.
Advantages:
- strength is about ten times higher;
- thermal conductivity is lower - 0.028-0.034 W / (m ° C);
- practically zero water absorption, therefore, when insulating with extruded polystyrene foam, there is no need to use vapor and waterproofing;
- as a rule, penoplex belongs to the third flammability group, i.e. is a low-combustible material due to the presence of a flame retardant in the composition.
Extruded polystyrene foam is far from always a low-combustible material, so when choosing a heater, pay attention to this point.
Flaws:
- low vapor permeability - this indicator is slightly higher than that of polystyrene, but still not enough for the material to be called "breathable";
- high price - penoplex is the most expensive insulation.
Price. Depends on the manufacturer:
Option 3: basalt wool
Most often, attic insulation is carried out with stone wool. This material is made from basalt rocks and hydrophobic additives that serve as a binder.
Advantages:
- environmental friendliness - basalt wool made from natural materials;
- high coefficient of vapor permeability, due to which, after the roof is insulated, a favorable microclimate will remain in the room;
- does not burn at all and has good fire resistance, i.e. resists the spread of fire;
- ease of installation - mineral wool is sold in the form of rolls and slabs (mats);
- thermal conductivity is slightly higher than that of expanded polystyrene, but still the thermal insulation qualities are high level- 0.032-0.039 W / (m ° C).
Do not confuse stone wool with slag or glass wool. Insulation of the mansard roof of a private house is best done with basalt wool. Only it can be considered an environmentally friendly material. In addition, it has higher characteristics than slag and glass wool.
Flaws:
- absorbs moisture, therefore, during installation, it is necessary to provide high-quality vapor and waterproofing;
- working with mineral wool with your own hands is not comfortable, as it causes irritation on the skin. Therefore, when working, use personal protective equipment;
- the cost is higher than the price of foam.
Despite these shortcomings, in my opinion, stone wool is the best insulation for the attic roof.
Price. The price of stone also depends largely on the manufacturer:
The denser the stone wool, the more expensive it is, therefore it is more expedient to choose a heater with a density of less than 100 kg / m 3.
Option 4: polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is another polymeric insulation. Unlike the materials described above, it is applied liquid, i. in the form of foam.
Advantages:
- thermal conductivity is the lowest - according to manufacturers, this figure is 0.019 - 0.028 W / (m ° C). This indicator is due to the fact that the polyurethane foam cells are filled with a gas that has even lower thermal conductivity than air;
- due to application in liquid form, forms a continuous surface without cold bridges;
- has good adhesion, due to which it sticks to any surfaces;
- resistant to moisture, so it does not require vapor-waterproofing;
- due to the presence of a flame retardant in the composition, the insulation does not burn.
Flaws:
- it will not be possible to perform insulation on your own, since this procedure requires special equipment. Moreover, the instructions for applying insulation are quite complicated, therefore, for the quality of the work, you should have certain skills;
- the material has zero vapor permeability;
- over time, thermal conductivity increases, as the gas leaves the shell of polyurethane foam;
- in liquid form, polyurethane foam has an unpleasant odor, and it is toxic. True, the foam dries very quickly and becomes completely safe for health;
- the cost of polyurethane foam, taking into account the work, is quite high.
For these reasons, polyurethane foam is more often used for outdoor insulation of housing. However, it can also be used to insulate the roof from the inside. If your choice fell on him, do not forget to provide good ventilation.
Price. For different companies involved in polyurethane foam insulation, the cost of services and the material itself may be different. However, the average price is - 450-500 rubles. 1m3.
Option 5: ecowool
Name of this thermal insulation material speak for itself - its main advantage lies in environmental friendliness. The basis of the material is cellulose, which occupies 80% of the composition. The raw material for it is the waste of cardboard and paper production.
In addition, the composition contains boric acid, which acts as an antiseptic, as well as sodium tetraborate, a strong fire retardant.
It should be noted that there are three ways to install ecowool:
- Hand dry. This method is suitable for warming horizontal surfaces, for example, they can insulate the attic floor. In this case, the space between the beams is filled with dry ecowool, which is sold in bags;
Application of ecowool in a wet automatic way
- Automatic wet glue.
This method resembles the application of polyurethane foam. Principle this method is that ecowool is applied in liquid form under pressure. Due to the adhesive composition, the insulation adheres well to the surface, as a result of which it can be used to insulate the roof of the attic.
Therefore, in our case, this method is the most optimal. Moreover, it is he who is most effective due to the uniform material.
Advantages:
- low thermal conductivity - 0.032 to 0.041 W / (m ° C);
- applied in a continuous layer, due to which cold bridges are excluded;
- thanks to the flame retardant does not burn;
- ecowool is resistant to biological influences as well as all the heat-insulating materials described above;
- light weight - density is 35-55kg/m3;
- is environmentally friendly not only in dry, but also in liquid form;
- refers to "breathable" materials.
Flaws:
- during operation, it greatly decreases in volume (up to 20%), as a result of which its thermal conductivity increases. Therefore, insulation should be applied with an excess of 20-25 percent;
- absorbs moisture, therefore, it needs high-quality vapor and waterproofing;
- it will not be possible to perform the insulation yourself, as this requires equipment. In addition, in order to avoid a strong increase in thermal conductivity, it is necessary to have a good experience with ecowool.
- when applied wet, it dries for a long time - from 48 to 72 hours. The drying speed is affected by the thickness of the layer.
An exception is the insulation of the floor;
Do not place ecowool in close proximity to heat sources such as chimneys. This can lead to its gradual smoldering.
Price. The price of insulation with a wet-glue method, taking into account the work, is on average about 1900-2000 rubles per cubic meter. A bag of dry ecowool weighing 15 kg costs about 500 rubles. Do not forget that the selected insulation still needs to be delivered, which means that transportation costs will be added to its cost.
Conclusion
We got acquainted with all the main pros and cons of thermal insulation materials that can be used for insulation attic floor. To make the final choice, watch the video in this article. If you have any questions - ask, I will definitely answer them » width="640" height="360" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen">
Conclusion
We got acquainted with all the main pros and cons of thermal insulation materials that can be used to insulate the attic floor. To make the final choice, watch the video in this article. If you have any questions - ask, I will answer them.
Completed the second floor, but do not know how to insulate it? I will talk about the choice of insulation for the attic. And for dessert, we will consider 6 types of heat-insulating materials that are suitable for these purposes, get acquainted with their properties, advantages and disadvantages.
A few words about choice
First of all, let's figure out how to choose a heater? In fact, everything is quite simple, you just need to consider when choosing some important requirements for the material:
- Durability. In my opinion, modern material should serve for several decades;
- Environmental friendliness. Insulation must be safe for health - this is one of the main requirements;
- Efficiency. The higher the thermal conductivity, the greater should be the thickness of the insulation layer;
- Shape saving. Thermal insulation should not shrink so that cold bridges do not occur;
- Noise isolation properties. Especially important for roofs covered with steel materials (profiled sheet, seam roofing, etc.);
- Affordable cost. Often homeowners have limited budgets. Therefore, the price / quality ratio can play a decisive role in the choice.
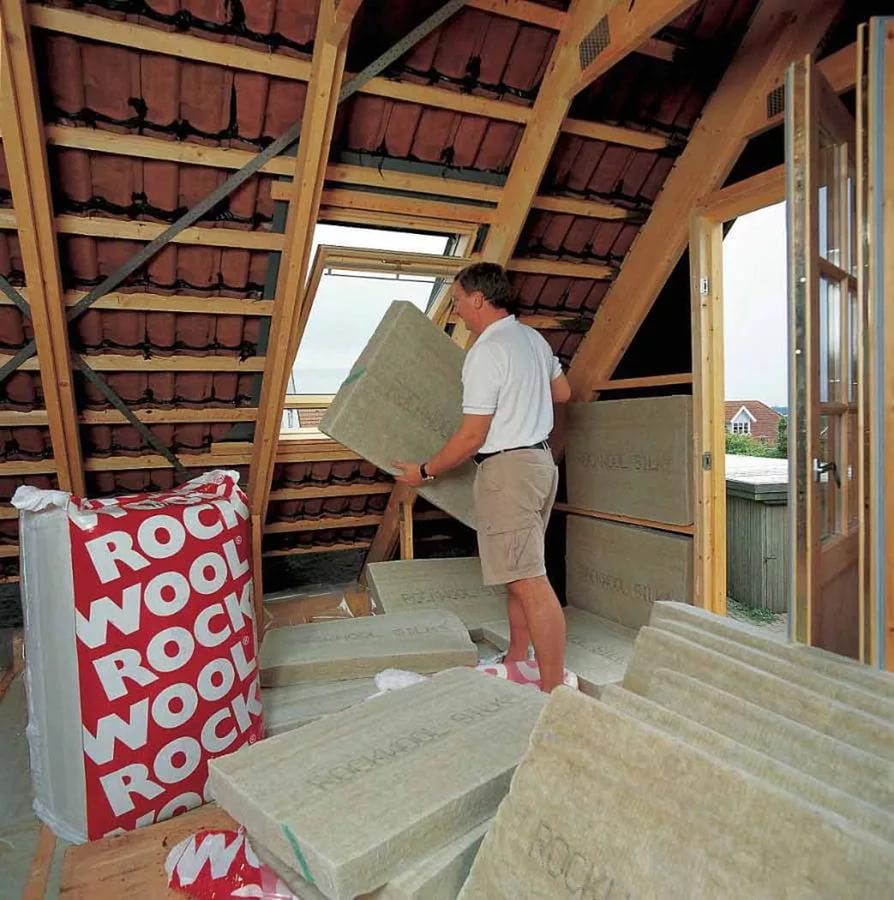

Also keep in mind that all types of heaters that are suitable for attic insulation can be divided into two types:
- Slab. They allow you to perform the insulation of the mansard roof on your own, as they do not need the use of additional equipment;
- Sprayable. Attic insulation requires special equipment. Insulation in this case is carried out by specialists, which entails additional costs. This method of thermal insulation has its advantages, which I will discuss below.
Plate heaters
Plate heat-insulating materials include:
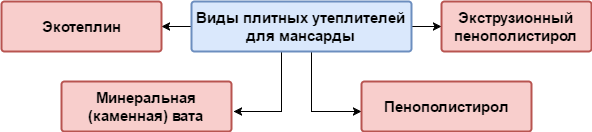
Option 1: mineral wool
Today it is the most popular mansard roof material that meets all requirements. It is a compressed fiber from the melt of rocks. The highest quality wool is made on the basis of basalt.

Unlike the well-known glass wool, which was widely used in Soviet times, basalt wool practically does not cause skin irritation and allergies. It is more environmentally friendly, and it is more comfortable to work with it.
Advantages of mineral wool:
- Fire resistance. Stone wool is the only slab insulation that does not burn and is able to withstand high temperatures for a long time;

- Vapor permeability. The material passes steam well, as it has a fibrous structure. This property also favorably distinguishes mineral wool from most other plate materials.
At the same time, stone wool is much more moisture resistant than glass wool;
- Durability. Stone wool can last over 60 years;
- Environmental friendliness. As part of stone wool does not contain formaldehyde and other components hazardous to health. True, this applies only to material from well-known manufacturers.
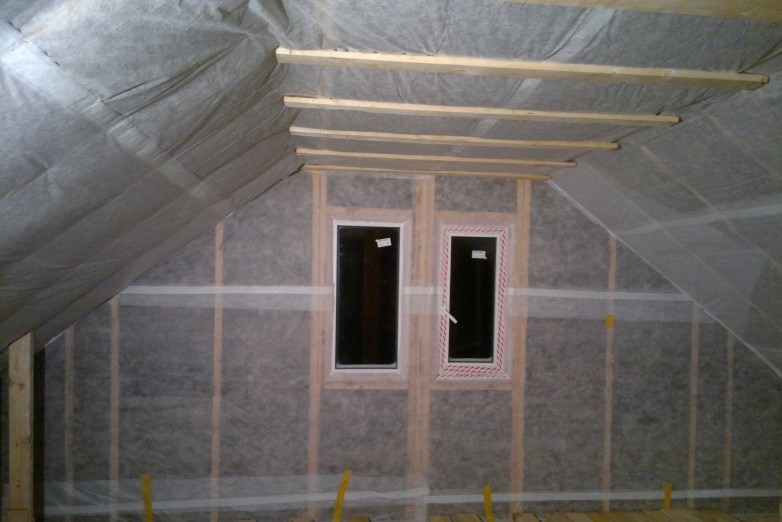

Flaws:
- Moisture absorption. According to this indicator, mineral wool is inferior to polymeric materials. Therefore, during its installation, a hydro-vapor barrier is always used.
In addition, when laying the plates, it is necessary to provide ventilation gaps that allow moisture to evaporate; - High price. Mineral wool is relatively expensive, especially for basalt wool.
Despite these shortcomings, in my opinion, mineral wool is the best insulation for a mansard roof. The only thing is that it just needs to be installed correctly.
Characteristics:
The density of mineral wool, as you can see, is different. To insulate a mansard roof, it is advisable to use a heater with a density of 90-100 kg / m3. It does not shrink and at the same time is effective in terms of thermal insulation.

Price:

Option 2: ecoteplin
Ecoteplin is a board made from flax. Sometimes the insulation is made on the basis of hemp, sheep wool or other natural materials. Outwardly, they are not much different from the stone wool described above.
- Efficiency. The thermal conductivity of ecoteplin is even lower than that of mineral wool;
- Vapor permeability. Like mineral wool, this material is classified as "breathable";
- Fire safety. Thanks to special impregnations, ecoteplin only smolders, therefore it belongs to low-combustible materials.
- Biostability. This quality is due to the use of impregnations in the manufacturing process of insulation.
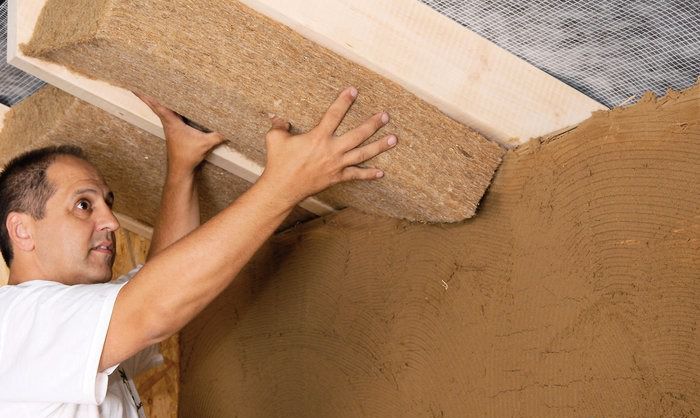

Flaws: Of the minuses of ecoteplin, it can be distinguished that it strongly absorbs moisture. True, the material dries quickly, and returns its thermal insulation qualities.
This insulation is quite rare in hardware stores. But it is easy to find it in online stores.
Characteristics:
Price. The price of ecoteplin averages 2500-3000 rubles. for 1m3.
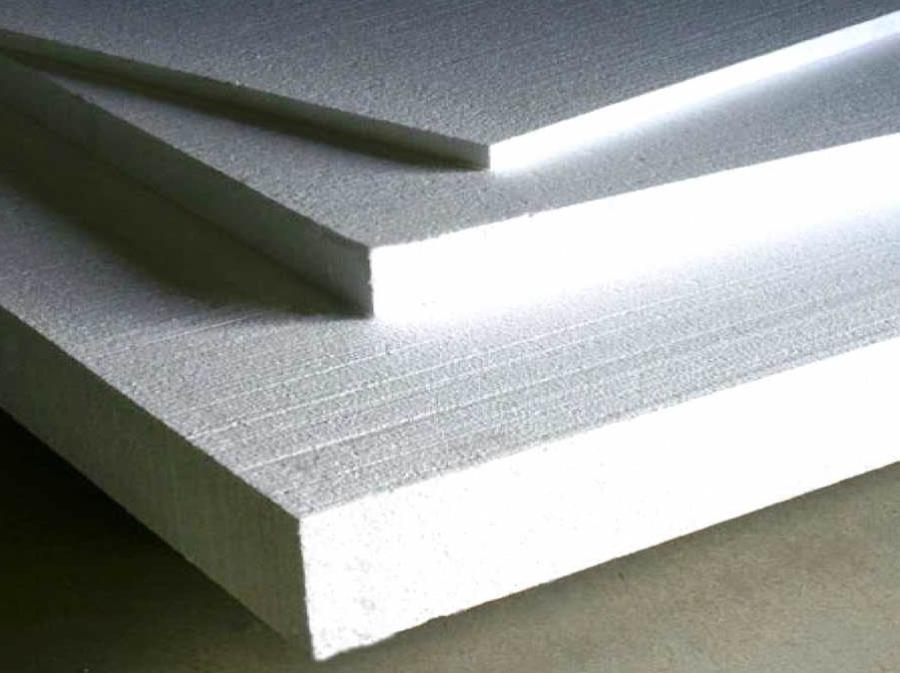

Option 3: Styrofoam
Polyfoam is a polymeric slab insulation. It has a granular structure, consisting of small granules glued together. The latter are filled with air.
Styrofoam received wide application due to low cost. It is the cheapest not only among polymeric, but also in general of all existing plate heaters.
Advantages:
- Light weight. The maximum density does not exceed 35 kg/m3;
- Durability. Styrofoam can last up to fifty years;
- Efficiency. The thermal conductivity coefficient of this thermal insulation material is lower than that of mineral wool.

Flaws:
- Doesn't "breathe". When insulating, it is necessary to qualitatively protect the insulation and wooden structures from moisture from the inside. Otherwise, water will accumulate between the insulation and rafters or other wooden parts, which will cause them to rot.
I must say that this minus applies to all plastic materials, so I will not mention it further; - Flammability. In order to save money, manufacturers rarely add fire retardants to the composition of the foam, as a result of which it burns well;

- Toxicity. Under the influence of high temperature, polystyrene foam releases dangerous toxins;
- Moisture absorption. Styrofoam absorbs moisture quite strongly compared to other plastic heaters.
For these reasons, it makes sense to use foam only when the budget is very limited.
Characteristics:
Price. The price of PSB-S-25 plates is about 2000 rubles. for 1 m3.

Option 4: foam
Extruded (extruded) polystyrene foam, or penoplex, is a polymer plate insulation made from the same raw materials as the foam. In its manufacture, a special technology is used, as a result of which this insulation is better than polystyrene foam in many ways.
Advantages:
- Strength. It has a more uniform structure, and has a higher density. As a result, its strength is about 10 times that of foam;
- Efficiency. The thermal conductivity is slightly lower than that of polystyrene, which makes penoplex one of the most effective heaters;
- Moisture resistant. This thermal insulation practically does not get wet;

- Fire safety. As a rule, penoplex refers to low-combustible materials, which is achieved by adding fire retardants to its composition;
- Durability. It can last more than fifty years.
Flaws. Of the minuses, one can single out the high cost of this heater.
Characteristics:

Price:
Spray materials
With sprayed materials, as I said above, it will not be possible to insulate the attic with your own hands. But on the other hand, they have one advantage over slabs - they are applied to the surface in a continuous layer. As a result, cold bridges are excluded, so there is also a certain sense in their use.
The sprayed materials include the following heaters:
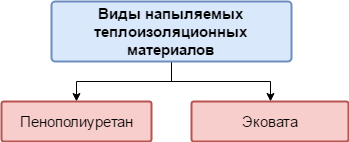
Option 5: polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is a polymeric material that is sprayed in the form of foam. Like other polymer heat insulators, it has a cellular structure. Moreover, its cells are filled with gas.
Advantages:
- Moisture resistance. This mansard roof insulation does not need a vapor barrier;
- Strength. After hardening, it forms a “shell” on the surface that is resistant to mechanical stress;
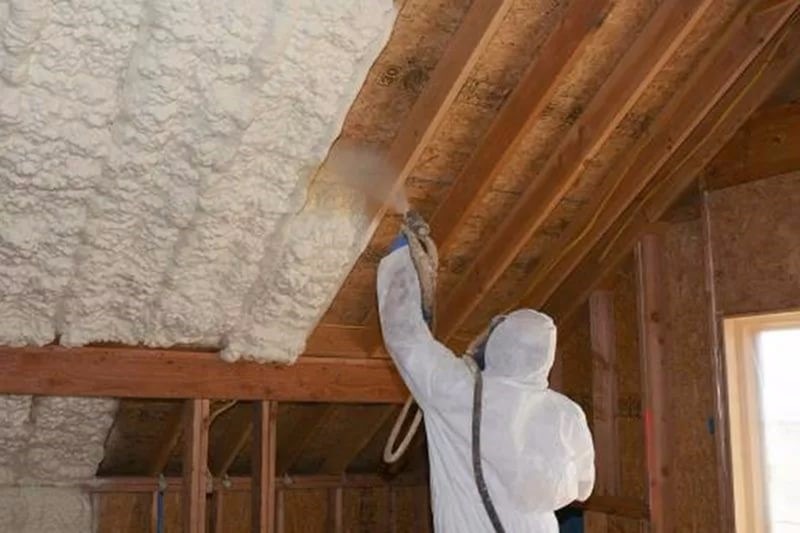

- Good adhesion. This allows you to spray polyurethane foam on any surface;
- Durability. Serves at least 30 years;
- Fire safety. Flame retardants are added to the composition of polyurethane foam.
Flaws:
- Difficulty of application. Warming must be carried out by qualified specialists. For such services, it is better to contact large companies without trying to save money;
- High price. This method of insulation is one of the most expensive;
- Toxicity. The foam has a strong toxic odor. True, after solidification, the material is absolutely safe for health;

- Increase in thermal conductivity. The gas eventually leaves the cells and they fill with air. This leads to some decrease in the efficiency of the insulation.
Characteristics:
Price. Average insulation square meter surface with polyurethane foam costs 500 rubles.

Option 6: ecowool
For those who want to make their housing environmentally friendly, ecowool is a good alternative to ecoteplin. This cotton wool is made on the basis of cellulose. As a rule, the raw material for it is newsprint.
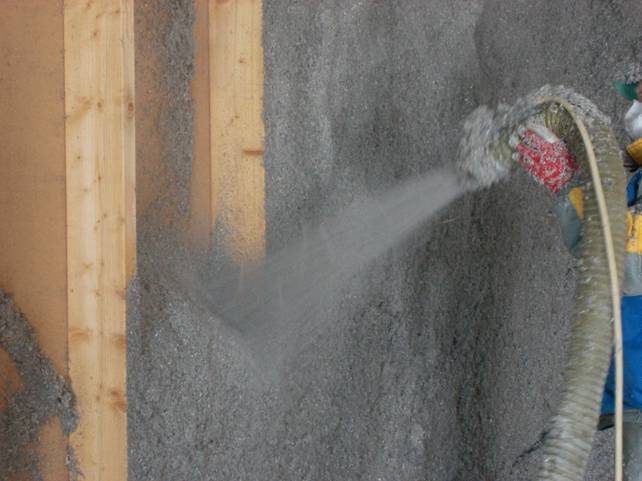

I must say that the insulation of the attic can be done in several ways:
- Wet spray method. In this case, the cotton wool mixed with the adhesive composition is supplied under pressure;
![]()
- Dry way. This technology is applicable only to frame structures, in particular, roof insulation can be performed in this way. Its essence boils down to wrapping the frame with a film, and filling dry cotton wool into the space of the frame through a hose;
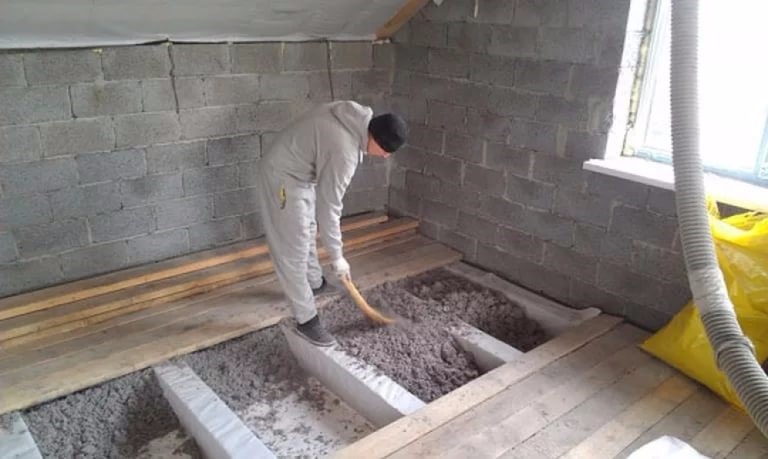

- Manual. This technology allows you to insulate only wooden floor. The instructions for warming are extremely simple - cotton wool is simply poured between the beams and leveled.
Advantages. The main advantage of ecowool is its environmental friendliness. Also, the material has other advantages:
- Vapor permeability. According to this parameter, ecowool is not inferior to ecoteplin;
- Fire safety. Does not ignite;
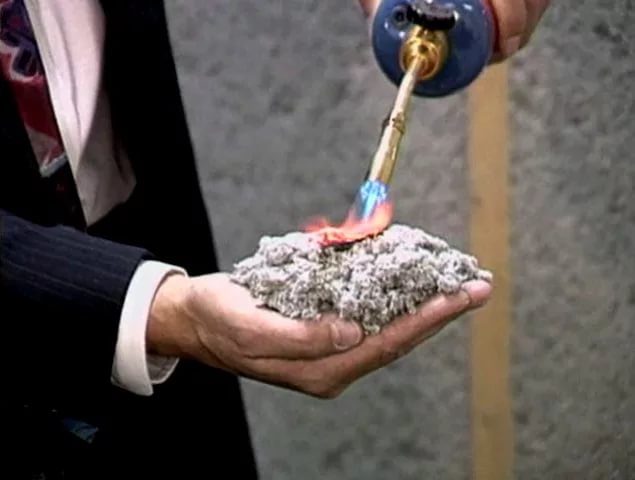

- Biostability. Ecowool does not rot, rodents and insects do not start in it;
- Durability. This attic roof insulation can last more than 60 years.
Flaws:
- Dries for a long time. Cotton wool can dry out for several days;
- Shrinkage. May exceed 20 percent. Therefore, ecowool should be applied in excess;
- Moisture absorption. Cellulose wool needs high-quality waterproofing.
Characteristics:
Price. A cube of cotton wool, when insulated by spraying, costs an average of 2000 rubles, 15 kg of dry cotton wool costs about 500 rubles.
That's all I wanted to tell you about heaters. Also, I explained which one is better.
Conclusion
Now you know what insulation can be used for the attic and what characteristics and properties they have. Watch the video in this article for more. If some points are not clear to you, write comments, and I will definitely answer you.
The question of which insulation is best for the attic is relevant for those who decide to equip a living space under a high pitched roof of a private house. The attic differs from the usual room of the house in increased heat loss. This is due to the fact that usually it does not have capital external walls without window openings, and on both sides and from above the room is separated from the street only by a roofing system of small thickness.
Mineral wool insulation
Criteria for choosing a heater for the attic
High-quality insulation allows you to make the attic suitable for year-round use. When choosing a heat insulator, it is necessary to pay attention to performance characteristics materials, including compare :
- soundproofing properties;
- ease of installation;
- moisture resistance;
- resistance to biological destruction;
- lifetime;
- profitability;
- environmental friendliness;
- fire safety.
But the main quality by which the material for insulation is evaluated is its coefficient of thermal conductivity, on which the ability to retain heat in the room depends.
From the point of view of ease of installation and use of insulation, preference should be given to universal materials. If the same heat insulator can be used for walls, roofs and floors, the insulation of all structures will last the same period.
Soundproofing properties are a particularly important parameter if the roofing is made of metal (folded roof, metal tiles, corrugated board). Gusts of wind, rain and hail make such a roof “sound”, and staying in the attic will cause discomfort.
 Plate heaters of a well-known manufacturer
Plate heaters of a well-known manufacturer Since the roof frame is usually made of wood, it is desirable to use a fire-resistant and non-flammable insulation. Otherwise, an accidental fire will lead to the fact that the entire attic and roof will quickly be engulfed in fire.
To on wooden structures truss system and gables did not form condensate and the insulation did not lose its thermal insulation properties due to moisture penetration, it is necessary to insulate the attic room with vapor and moisture-proof material, or use reliable hydro and vapor barrier. This affects the speed and complexity of the installation of the insulating layer, affects the preferences when choosing a material.
Insulation thickness
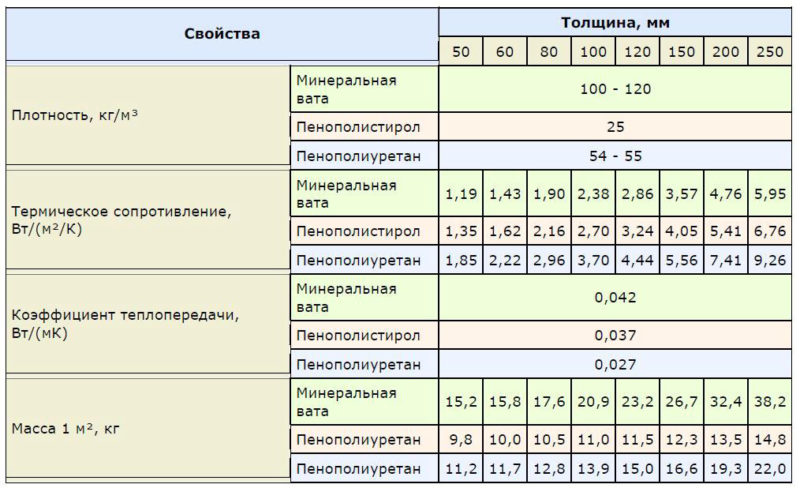
Table 1. The dependence of the thickness of the insulation on the coefficient of thermal conductivity
The manufacturer indicates the thermal conductivity coefficient on the packaging of the material. This indicator depends on the production technology and the density of the insulation. The table below shows the average values:
Table 2. Thermal conductivity coefficients of some heaters
Polyurethane foam and ecowool - modern materials, which can be used as a heat insulator for attic rooms, but their installation requires the use of specialized equipment, the invitation of specialists. The rest of the popular heat insulators are available in the form of plates or roll materials of various densities and thicknesses.
The insulation is cut along the width of the span between adjacent rafter legs (or the gap between the laths of the lathing on the walls) and inserted by surprise. If the calculated thickness of the thermal insulation layer exceeds the width rafter leg, bars of a suitable section are stuffed onto the rafters from the side of the room.
Two-layer insulation is considered the most effective - after the gaps between the rafters are filled with a heat insulator, another layer of roll material (possible with a foil vapor barrier outer surface) is attached over the rafters with continuous joined strips. This will prevent the formation of cold bridges.
 Laying a heat insulator between the rafters
Laying a heat insulator between the rafters Let us consider in more detail the main pros and cons of popular heaters that are suitable for thermal insulation of the attic roof and gables.
Fibrous roll and plate heaters
- glass wool;
- mineral wool;
- stone (basalt) wool.
Their key advantage and at the same time a disadvantage is the ability to pass steam. Theoretically wet. warm air it will leave the attic through a breathable inner lining, heat insulator and roofing system, which will help maintain a favorable microclimate in the room. In practice, there are the following difficulties:
- an increase in the moisture content of the fibrous insulation leads to a sharp decrease in its thermal insulation properties;
- the insulation that has accumulated moisture (especially glass wool) is crushed, deformed, forming cold bridges;
- the wood of the truss system begins to rot from contact with moisture.
To avoid these problems, it is necessary to mount a vapor barrier on top of the insulation from inside the room. And between roofing and thermal insulation must be laid waterproofing material.
 Roofing pie with waterproofing over insulation
Roofing pie with waterproofing over insulation Air exchange through fibrous insulation will be carried out only if the waterproofing and vapor barrier layer is made of special gas-permeable membranes. The vapor barrier must allow air to pass through, but retain moisture coming from the room. A gas-permeable waterproofing barrier must release moisture from the insulation, and prevent water from entering it.
Membrane materials are much more expensive than ordinary or reinforced film, roofing felt or glassine. But these investments will justify themselves due to the durability of not only insulation, but also the roof truss system.
 Super diffusion membrane
Super diffusion membrane If a film is used as a vapor barrier, this will reduce the cost of construction, but this will nullify an important advantage of fibrous insulation - gas permeability. Perforated film should not be used, as it allows steam to pass through, which will accumulate in the insulation.
Performance characteristics of fibrous insulation
glass wool. Its positive qualities include:
- fire safety (2nd degree of fire resistance);
- environmental safety (does not contain resins);
- unattractive for mice (do not build nests and moves);
- affordable price.
The main disadvantage is that when working with the material, sharp glass dust is formed, the installation of a heat insulator requires accuracy and the use of protective equipment. In addition, over time, glass wool tends to deform, wrinkle, especially when moisture penetrates.
Mineral wool. The composition of the material includes fibers of various origins (production material - clay, stone, quartz sand, glass, etc.). Mineral wool is characterized by a multilayer inhomogeneous structure with air lenses. Due to this, the material dampens sound waves well. Mineral wool (primarily Isover, Ursa) is recommended for those who decide to make metal roofing.
Such a heat insulator is fire resistant, does not rot, and is easy to install. But rodents can settle in it, whose nests, passages and waste products reduce the performance properties of the insulation.
Basalt wool. Consists of fibers obtained by melting rock. Withstands heat up to 1000 degrees, does not spread combustion. Basalt wool should be chosen carefully, checking quality and safety certificates: some manufacturers, in an effort to reduce the cost of products, use resins that emit toxic substances.
 Basalt wool
Basalt wool Basalt wool is resistant to fungus, but can be damaged by rodents. This is a good sound insulator, easy to install. But when choosing a material for insulating the truss system, one should take into account the rather large weight of stone wool slabs.
If you have to choose a fibrous heat insulator, pay attention to the density of the material. The heat insulator should not lose shape even during prolonged use. For mineral, basalt wool, the density index should be about 40-45 kg / m3.
Polymer materials for insulation
We choose a polymer heat insulator for the roof and walls of the attic. This can be polystyrene foam, extruded polystyrene foam (these two types of insulation are available in the form of sheets and plates of various thicknesses), as well as polyurethane foam, which is applied to structures by spraying.
The advantages of polymer insulation include low weight and low thermal conductivity. Such thermal insulation will not overload truss system and successfully cope with the task of keeping warm.
The disadvantages of polymer insulation include extremely low vapor permeability. Gas exchange is not carried out through insulated structures, therefore, one cannot do without a well-thought-out ventilation system in the attic room.
 Attic insulation with polyurethane foam
Attic insulation with polyurethane foam Thermal insulation made of extruded polystyrene (foam) and polyurethane foam will not allow heat and steam to pass to the roof truss, therefore, there is no need to install a vapor barrier from the side of the room. Despite the fact that the dew point during the internal insulation of the gables will shift towards the heat insulator, moisture dangerous for wood will not condense.
All joints and junctions of thermal insulation made of foam plastic must be filled mounting foam and (after removing excess foam) are glued with reinforced tape so that the insulation layer is airtight.
Manufacturers produce penoplex of various densities. For pitched roofs and attic walls, where heat losses are high, it is advisable to use slabs with a density of 30-35 kg / m3.
If you decide to choose an inexpensive foam plastic, it is better to mount the insulation according to the same principle as fibrous plate materials. Unlike extruded polystyrene foam with a solid closed cell structure, the foam consists of many individual pellets compressed into a board. Between building blocks there are technological pores that are able to pass steam to wooden structures.
A suitable foam density is 35 kg/m3, the material must not crumble into individual balls when broken. Since the foam plastic smolders when ignited, releasing toxic substances and mice easily gnaw through it, this is not the most best material for internal insulation.
Polymer insulation for the attic should not be considered as a soundproofing material for the roof - it will not save you from the sound of raindrops. But if you insulate the floor with it, it will reduce the vibration load from steps, creating acoustic comfort in the rooms under the attic.
The selected insulation option will serve long years if purchased good stuff and take into account all the subtleties of its installation.
The popularity of lofts is growing rapidly. For developers, this type of housing seems to be less expensive in comparison with the cost of equipping storey premises. In addition, many homeowners are attracted by the opportunity to implement specific architectural and design solutions, substantively developed by European specialists. Why did the transfer of under-roof zones into housing stock become actual in our country only in the last 10-15 years? The answer lies in the climatic difference between continental Europe and the European part of the Russian Federation. Only modern technologies in the field of insulating materials are doing possible choice insulation for the attic, providing a comfortable microclimate in a "house without walls", located somewhere in the suburbs.
It is important to choose the right insulation for the under-roof space
The arrangement of mansard roofs is functionally and technologically different from the work carried out on the main floors and in unheated attic spaces. Attic insulation is associated with increased complexity of installation processes, the need for thermophysical calculations, as well as the importance of competent development of ventilation and vapor protection.
In non-residential attic spaces, thermal insulation is laid in niches between the beams of the ceiling. The roof structure in this case plays the role of a barrier that protects the building from wind load, temperature expansion and precipitation. Insulation for the mansard roof, on the contrary, is part of roofing sandwich, designed to immediately perform all the functions inherent in walls, ceiling and roof.
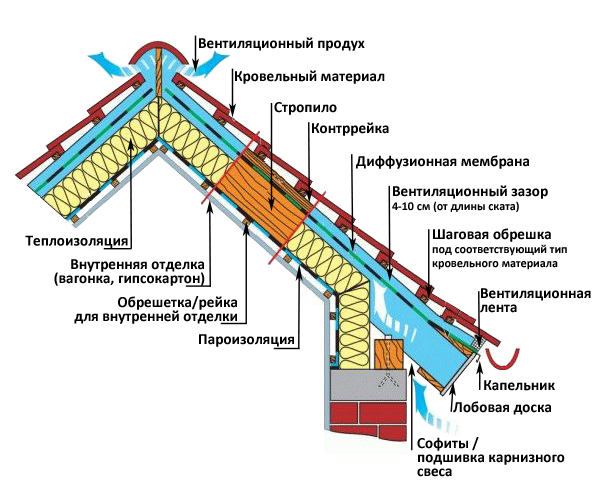
Enters the attic more moisture than in storey rooms. Water in the form of ascending vapor penetrates from below. The vapor barrier of the floor ceiling reduces the flow of moisture, but does not nullify it.
The second factor in air humidification is associated with the inevitable condensation on the lower surface of the tiles or other roofing material. Moreover, the amount of this condensate on insulated roofs is greater than on cold ones due to the increased temperature gradient. Also, ventilated cold attic forms a buffer air cushion that effectively dries the roof from below. The absence of such a buffer in the attic reduces the natural ventilation of the wooden rafters and the insulation itself.
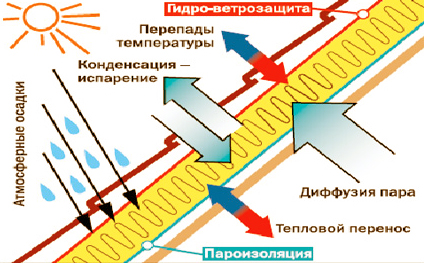
The location of thermal insulation directly under the roof slopes increases the intensity of heat transfer, so attic insulation should be more energy efficient than floor insulation between housing and a cold attic.
Criteria for the selection of insulating material
What is the best way to insulate an attic? The study of the properties of heat insulators cannot give a reasonable answer to this question. It is necessary to correlate the characteristics of materials with the conditions of their work. The specificity of attics is expressed in three main rules for their insulation:
- Terms of performance of thermal insulation works. Usually freshly sawn wood is used for rafters. In this case, it is required to withstand at least six months before the insulation is carried out with materials with high vapor permeability.
Even when using dried wood, a pause of at least 2 weeks is necessary after the installation of the roofing.
- Choice of insulation thickness. The intensity of heat flows through the roof is much greater than the loss of energy through walls or foundations. The usual thickness of mineral wool of 100 - 150 mm does not solve the problem for attic insulation even in the southern regions of Russia. It is necessary to use special calculator programs, where climatic conditions, dimensions are substituted building structures and materials of all layers of the sandwich. In temperate continental climates, the required design thickness of an insulator for a mansard roof is almost never less than 300 mm.
- Design of roof beams.
The height of the lumber profile should be 30-40 mm higher than the thickness of the heat-insulating layer. In this case, a sufficient ventilation gap is formed between the waterproofing and the insulation.
If work is underway to convert a cold attic into a housing stock, then an additional crate from the bottom of the rafters is usually used, increasing the installation height to accommodate the insulation layer.
To determine which insulation is best for your mansard roof, make a comparative assessment of the materials, taking into account the three rules outlined in the following order:
- Eliminate options that do not meet your fire safety requirements.
- Exclude options with high vapor permeability of the insulation if you do not have time to dry the wood of the rafters.
- Calculate the required insulation layer thickness for several options.
- Make budget options. In this case, one should take into account the exclusion of a vapor barrier membrane from the composition of the sandwich in the case of using insulating materials with a hygroscopicity close to zero.
Types of insulation materials used for mansard roof insulation
First of all, it should be noted that it is not only inconvenient, but also impractical to insulate inclined surfaces with bulk materials, since the fragments rolling down will block the ventilation gap. Therefore, sawdust, fluff pulp, expanded clay and similar heaters should be discarded. On the other hand, it is permissible to conduct insulation with plates obtained as a result of a mixture of the listed materials with clay or cement. However, taking into account roof trusses should lay the weight of such plates.
Fireproof heaters

The only relatively inexpensive fireproof heat insulator is mineral (basalt) wool. It is for this reason that she for a long time remains the most popular option for attic sandwich applications. How to choose a good mineral wool insulation for the attic? Will a regular roll isover that we use for walls work? Such material will work well, but ... not for long. The reason for this is high capillary activity. Therefore, it is necessary to choose materials with special impregnations that reduce hygroscopicity: mineral wool ROCKMIN PLUS, Izover pitched roof and other brands, in the names of which there is a direct indication of the field of application that suits us.
Mixtures of insulating backfills with clay are also fireproof. The main problem of clay insulation is the very large thickness of the insulating layer and its excessive weight.

Of the most modern developments, PIR boards lined with heat-reflecting foil should be highlighted. They do not support combustion and have a record low thermal conductivity (0.024 W / m * K).
Heaters with the highest energy efficiency
Manufacturers of building thermal insulation have developed grades of extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) boards, specially designed for arranging attics and roofs of cold attics. These are Penoplex Pitched Roof, TechnoNIKOL Carbon Solid and other materials with a thermal conductivity coefficient of not more than 0.030 - 0.034 W / m * K. The brands are distinguished by the ability to order panels of increased length (up to 4.5 m), which significantly speeds up installation work.
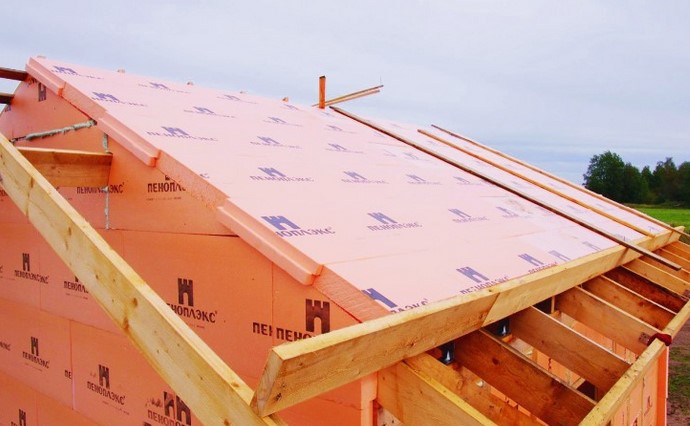

EPPS - combustible material, but building codes allow its use in attic equipment. To increase fire safety, infrared screens with a foil layer should be used. Despite the fact that their vapor barrier function is not needed by XPS, the foil can significantly increase the fire resistance of the sandwich.
On average, expanded polystyrene boards make it possible to reduce the thickness of the attic insulation layer by 20% compared to mineral wool. Heat-saving champions are sprayed polyurethane foam (PPU) and the already mentioned PIR boards. Due to the high toxicity of gases released during the thermal destruction of polyurethane foam, this material is not recommended for use in residential attic equipment. PIR boards do not have this drawback and are able to replace mineral wool with a 1.5-fold reduction in layer thickness.
Heaters with high specific noise absorption

Insulation with Zhivoizol - linen heat insulator
The soundproofing properties of mansard roof insulation can be very relevant when using metal tiles, which amplify the noise of natural precipitation. Currently, board materials have been developed that are characterized by a high noise reduction coefficient with a slight loss to mineral wool in energy efficiency. Among such developments, it should be noted pressed linen insulation, known under the market brands "Termolen" and "ZhivaIzol". Plates made of this material absorb noise in all frequency spectra 20% - 30% more efficiently than mineral wool and XPS.
Conclusion
The choice of insulation for the attic roof should be carried out in parallel with the development of roof trusses and the design of the entire sandwich, which includes roof cladding, membranes and battens. When converting cold attics into housing stock, it is relevant to minimize the thickness of the insulating layer and use insulators with the lowest thermal conductivity.
The wrong choice of insulation, or its insufficient thickness, leads not only to cold in the attic room. Even if you compensate for the low temperature with intensive heating, you may encounter:
- increased roof icing;
- reducing the life of the roofing;
- failure of the drainage system.
Thus, the competent design of a roofing sandwich for attics is important not only for providing comfort to residents, but also in terms of increasing the life of the building.
The charm and benefits of the attic room will come to naught if the walls freeze and become covered with black fungus. Apart from interior decoration, the insulation of this room is one of the main tasks. What is the best insulation for the attic? To make the right choice, you need to carefully understand its types and properties.
1 Which insulation is better for the attic - insulation methods
Based on the stage at which thermal insulation is planned, two methods are distinguished. outdoor method considered to be the best. and roofing is often carried out immediately, during the construction and facing of the house. External insulation helps to save inner space. Not suitable for insulating frame buildings.
Internal insulation is performed both in addition to external insulation (rarely), and when, for some reason, external insulation cannot be performed. Regardless of which method of insulation is chosen, it is worth considering:
- purpose of the attic. It is necessary to decide how often and in what period of the year it is planned to use this territory;
- climatic conditions of the region. The material for insulation must meet all requirements. It is important to take into account such phenomena as severe frost, sudden changes in temperature, high humidity;
- attic design - the number of windows, the slope of the roof, the thickness of the walls, etc. All these factors will help determine the level of insulation, its thickness and strength.
External thermal insulation is best entrusted to professionals who are well aware of all the subtleties of their work. But internal works you can do it on your own. Therefore, we will take a closer look at the second method. most often occurs in circular pattern- roof, facades, floor. Less common is the warming of one thing. To date, we have been given a huge selection of insulation for the attic - for any wallet. We hope that our article will help you decide what is the best way to insulate the attic.
2 The choice of insulation for the attic - selection rules
The purchase of materials must be treated with feeling, sense, arrangement. Having decided on the manufacturer and seller, before finally choosing a heater for the attic, it will not be superfluous to familiarize yourself with the certificates of conformity. Remember that the further success of the event depends on the quality of the purchased insulation.

To clearly understand what material to insulate the attic, one should take into account such characteristics as:
- Thermal conductivity of the material;
- Waterproof;
- Resistance to temperature extremes;
- Durability;
- Fire safety. The composition of the material must necessarily include substances that slow down the spread of fire (flame retardants);
- Environmental Safety.

Particular attention should be paid to the density of the material. Its structure must be strong and at the same time light. High-quality insulation when used should not change shape. The presence of defects and cracks indicates low-quality material. Using this in the future will lead to the need to redo all the work.
